Brochures - Canadian COVID-19 Antibody and Health Survey (CCAHS) – Cycle 2
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted our lives in many ways. In an attempt to better understand how COVID-19 has affected the health of Canadians, Statistics Canada, in partnership with Health Canada, the Public Health Agency of Canada and the COVID-19 Immunity Task Force, has created the Canadian COVID-19 Antibody and Health Survey (CCAHS). While this is a voluntary survey, your participation is important as your contribution will play an important part in understanding past infections by measuring the prevalence of COVID-19 antibodies amongst Canadians, including those who have never had symptoms.
What does participating in the CCAHS involve?
This unique survey will collect information in two parts.
- The first part is an electronic questionnaire about general health, chronic conditions and symptoms, access to care and exposure to COVID-19. The questionnaire must be completed prior to moving on to the second part as it is necessary to collect your personal information so we can send the results to you, and to obtain your written consent to complete the second part.
- The second part is an at-home finger-prick blood test which you will administer to yourself as soon as possible after completing the electronic questionnaire. You will then return the dried blood spot sample using the enclosed prepaid package. The lab will analyze the sample to determine the presence of COVID-19 antibodies.
How were you selected to participate in this survey?
You have been randomly selected to participate, which ensures that the data collected will be representative of the Canadian population.
Even if you do not think you have been exposed to COVID-19, your information will provide valuable answers about the virus. You will also receive a copy of your lab report, providing you with valuable information about your own health.
Why do I need to provide consent?
While completing the electronic questionnaire, you will be asked for consent to:
- provide the dried blood spot sample
- receive your test results
- store your sample in a biobank
- share certain data with provincial and territorial ministries of health, Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada and potentially McGill University.
By consenting, you confirm that:
- you understand that even though you have agreed to some or all of the items above, you can still withdraw from any part of this survey or subsequent studies at any time
- you understand what is involved in taking part in the survey.
Consent to storage of your samples
With your consent, the surplus dried blood spots samples (leftover blood samples after antibody testing is performed) will be stored anonymously at the Statistics Canada biobank located at the Public Health Agency of Canada's National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg. This is a high security facility that meets international security standards for this type of laboratory. The samples will be used for future health research projects. Only researchers who submit projects that meet the strict conditions imposed by Statistics Canada, in particular those relating to confidentiality, will have access to these samples.
Can I choose not to participate in the survey?
Your participation is voluntary. You can choose to end your participation in this survey (called withdrawal) at any time without having to provide a reason. If you choose to withdraw from the survey you can call us at 1-800-263-1136 (TTY: 1-800-363-7629) or email STATCAN.infostats-infostats.STATCAN@statcan.gc.ca. We will ensure that your samples are destroyed and your data deleted. If tests have already been done on your samples or your sample has already been sent to another laboratory for testing or related research, it will not be possible to withdraw those results. However, no further testing will be done.
What are the risks of participating in this survey?
You may experience very mild discomfort from the sting of the needle when taking a blood sample from a finger prick. Rest assured that we have chosen this measure and technique because it is safe. The risk of infection by COVID-19 from blood is considered extremely low. Medical research has shown that the virus is rarely found in the blood even when someone is sick. Furthermore, the small amount of blood that is being collected further minimizes any risk of infection. However you should still be cautious when handling blood because of the possible presence of other infectious agents.
What are the benefits of participating in this survey?
Your participation will help in further understanding the impact of COVID-19. The results will help indicate how many people have been infected with COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2), including those who may not have had related symptoms. Also, you will receive your test results once they are available.
Will my data be linked and shared?
When filling in the electronic questionnaire, we will inform you about the possibility of linking the information you provide to the CCAHS with other surveys or administrative data sources. Data linkage combines information on survey participants from at least two different sources. This is done only for statistical and research purposes. Linking data helps governments monitor, evaluate and modify policies in health care. If you agree to data linkage, we will:
- Ask you for your health card number to help with the linkage process.
- Combine the information we collect during this survey with some of the information that your provincial health department, health registries or other recognized health organizations already have on file about you.
- Remove personal identifiers such as your name, address and health card number from the linked file as soon as the linkage is complete.
- Destroy all linkage files at the end of the project.
Only Statistics Canada employees will perform data linkage. All linked data will remain confidential under the Statistics Act. We will not provide any information about you to the ministry of health in your province, territory or to any other organization. For more information on data linkage, visit Microdata Linkage at Statistics Canada
You will also be asked if you consent to sharing the information you provide with Health Canada, the Public Health Agency of Canada, and provincial and territorial ministries of health (including l'Institut de la statistique du Québec for Quebec residents). Sharing data allows researchers to fully utilize the information we collect to improve health policies and, in turn, the health of Canadians. If you consent, your data will be shared under the following conditions:
- Your name, address, telephone number and health card number could be shared.
- The Institut de la statistique du Québec and provincial and territorial ministries of health may make this data available to local health authorities. Local health authorities will not receive any personal identifiers, only your postal code.
- Your information will not be shared with any other party without your consent.
- Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada, and the ministries of health will use this information only for statistical and research purposes.
To avoid duplication of surveys, Statistics Canada might sign agreements to share the data from this survey with McGill University. McGill is the legal entity representing the COVID-19 Immunity Task Force (CITF). The CITF is a group of scientists and experts who use data to support decision-makers in their efforts to protect Canadians and minimize the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
With your consent, your survey responses and postal code will be shared with McGill and the CITF. Names, addresses, telephone numbers, email addresses and health card numbers will not be shared.
How will my data be kept private and confidential?
The data and samples are collected under the authority of the Statistics Act, which guarantees that all your personal information remains confidential and secure. Your data are also protected under the Privacy Act of Canada.
Statistics Canada will never:
- store or test your samples if you did not provide consent
- provide information about your samples to any law enforcement agency
- share your personal information or your test results with insurance companies or employers
- allow any of your information or data to be used in partnership suits or any other legal proceedings.
How do I do the dried blood spot (DBS) test?
This guide will demonstrate how to administer the dried blood spot (DBS) test. Please read the entire guide carefully prior to beginning the test. An instructional video can be found at Canadian COVID-19 Antibody and Health Survey (CCAHS). If you have any questions, please call us at 1-888-253-1087 or email statcan.ccahs-ecsac.statcan@statcan.gc.ca.
Statistics Canada takes all necessary precautions to ensure that the collection of health information and samples is safe for participants.
It is very important to note that you should not do the DBS test if you have a clotting condition such as hemophilia or Von Willebrand disease, if you have had chemotherapy within the last 4 weeks, or if you have undergone a bilateral mastectomy. If you have had a mastectomy only on one side, you may perform the finger prick on the opposite hand. In addition, you should not complete the DBS test if you have experienced fainting or vomiting due to a finger prick or the sight of blood.
If at any point you feel that your health or safety is at risk due to this test, please stop the test immediately. It is recommended that you administer the test with someone nearby in case you begin to feel unwell. Furthermore, if you are feeling stressed because of the survey or the COVID-19 pandemic in general, please visit Canadian COVID-19 Antibody and Health Survey and click on the Mental and Physical Health link under Participants for a list of tips and resources to help with your mental and physical health during these stressful times.
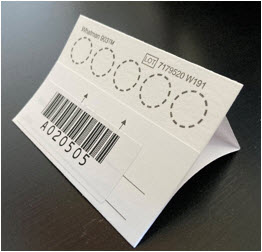
Before you begin, please make sure you have all the necessary items in your testing kit:
- 2 Single-use rounded T-shaped lancets
- 1 DBS card
- 2 Alcohol swabs
- 2 Gauze pads
- 2 Bandages
- 1 pair of gloves
- 1 Dehumidifying pack
- 1 Humidity indicator card
- 1 Small brown envelope
- 1 Large resealable plastic bag
- 1 Small striped plastic bag
- 1 Prepaid postage envelope

Step 1: Getting ready
- If possible, it is best to have another person present while you perform the DBS test. This is so that they can assist you in the event that you experience any adverse effects. They may also be able to help you with some steps of the process if required. Please note: if someone is assisting you or if you are assisting someone else with their DBS test, gloves should be worn to ensure that there will be no contact with another person's blood.
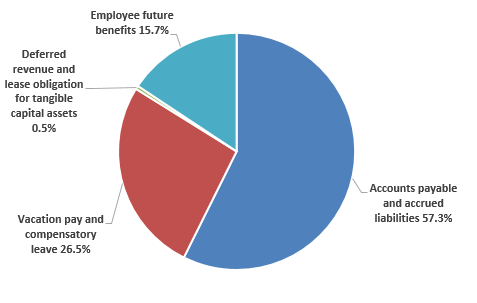
- Write the date in the space indicated on the small brown envelope. Do not write your name or any other information that could identify you. Do not write on the DBS card.
- Prepare all the materials before starting the collection, as shown in the picture below. We suggest covering the surface of the table with paper towels to absorb any excess drops of blood.
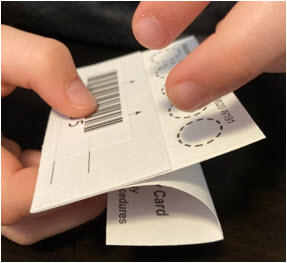
- Fold back the flap of your DBS card to uncover the testing area with the 5 circles. Make sure not to touch this area. Your card should look like the card on the photo below.
- Open the gauze package and a bandage and set aside. You will need these after pricking your finger with the lancet.
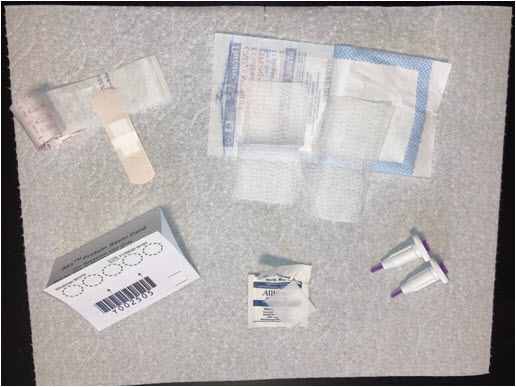
- Chose which finger you will be using to collect your sample. Only use your middle or ring fingers. It is important that you choose a finger that is not injured or infected.
- Make sure your hands are warm. This will improve blood flow. You can do so by rubbing your hands together or moving your arms.
Step 2: The collection
- Wash your hands with soap and water before and after the test.
- Make sure you are seated comfortably at a clean table with all provided materials within reach.
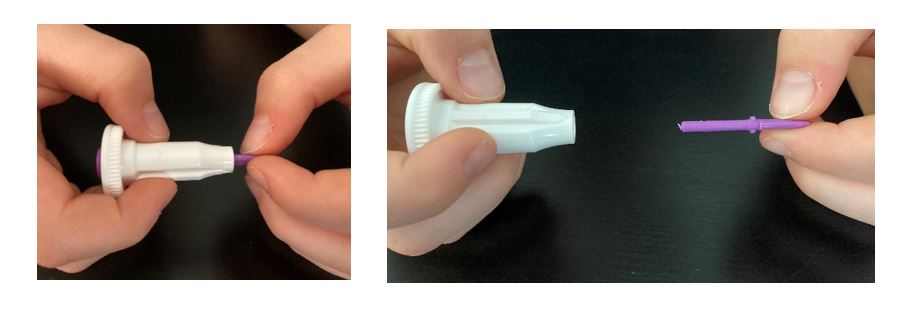
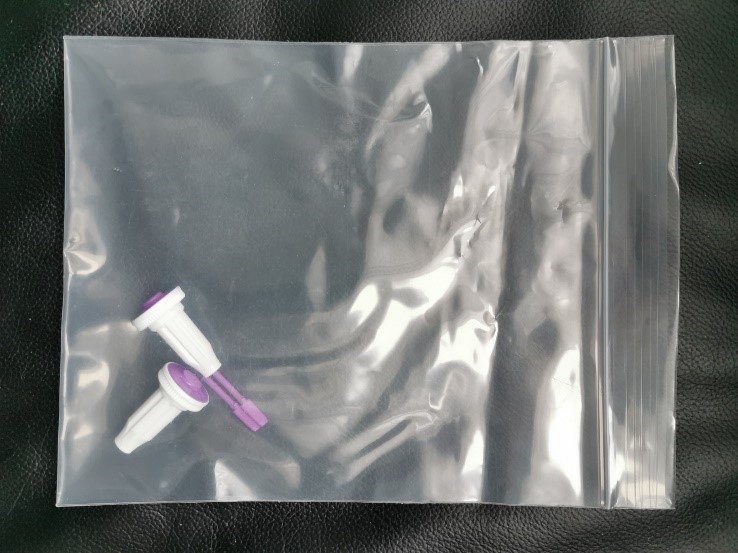
- Hold the white base of the lancet with one hand, and twist off the purple cap with the other. Even with the cap off, you will not see the needle. This is normal.
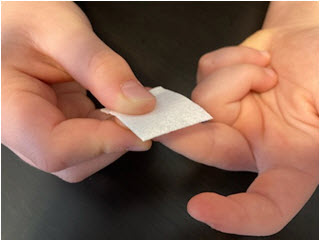
- Use the alcohol swab to clean the entire tip of the chosen finger all the way down to the first knuckle, and allow it to air dry.
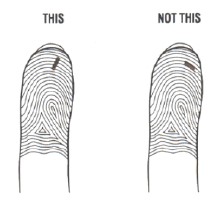
- Position the lancet on your finger tip. The needle should go across the fingerprint lines, not in the same direction.
- Lay the back of your hand against a solid surface:
Hold the lancet firmly between your index and major finger of the opposite hand, place the tip of the lancet onto the finger tip and push the button on the top of the lancet with your thumb. You will hear a click and feel it prick your finger.
Once a lancet is used, it retracts back into the device, and cannot be activated a second time. Two lancets have been provided in the event that you are unable to complete the test with only one finger prick. Should you choose to do a second finger prick, make sure to use a different finger.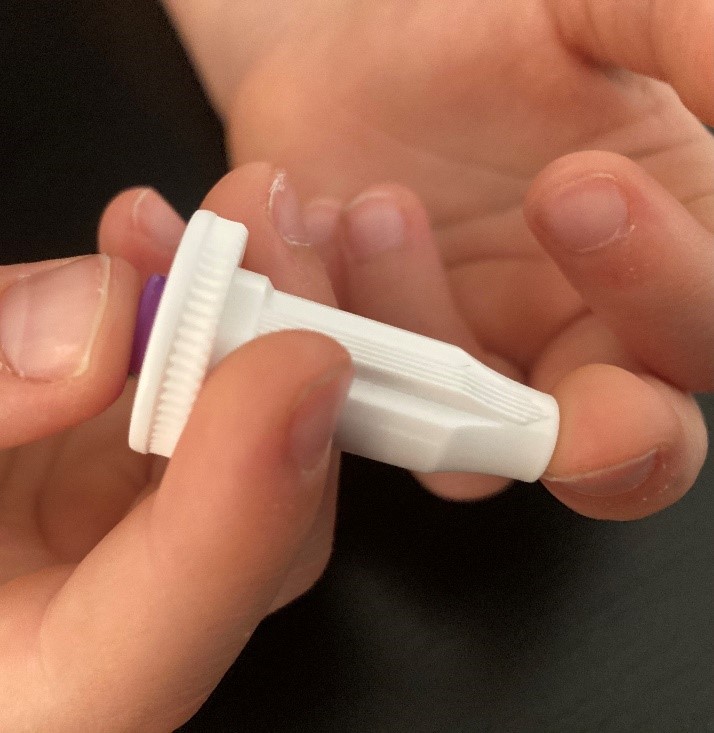
- Let a small drop of blood form at your finger tip and wipe it away with a gauze pad. Do not use the alcohol pad to wipe away the drop of blood.
- Now it's time to start collecting blood on the card. Gently squeeze your finger from the base towards the tip to help a blood drop form. Once a large drop of blood forms on your fingertip, let the blood fall from your finger onto the card. The blood should saturate the card and show through the other side. Do not let your finger touch the card.
Front of the DBS card
Other side of the saturated DBS card
Fill the first circle completely before moving on to the next. The goal is to fill all 5 circles, but fewer full circles are better than more incomplete circles. If one drop of blood is not enough to fill a circle, aim the next drop of blood beside the first drop until the circle is filled. Avoid layering blood drops directly on top of one another.
This photo demonstrates a good dried blood spot sample compared to a poor quality sample.
If you have attempted the DBS test, you should mail back your DBS card no matter the outcome. Even if you were only able to fill one circle, or if none of your circles are complete, the laboratory will still try to analyze your sample.
Step 3: After collection
- Apply firm pressure with gauze until the bleeding has stopped.
- Apply a bandage.
- Used lancets must be placed in the provided large resealable plastic bag and thrown in the trash.
- Place the DBS card in a safe place until it is completely dry. With the flap folded back, allow to dry for at least 3 hours. Do not place it in direct sunlight or near a heater, and keep out of reach of children and pets to avoid contamination.
- Once dry, fold the flap back over the blood spots and place it in the small brown envelope. Do not seal the small brown envelope. Place the small brown envelope, the humidity indicator card and the dehumidifying pack inside the small striped plastic bag. Do not place the humidity indicator card in the small brown envelope. Remove as much air from the bag as you can before closing it.

- To send your DBS test to , place your small striped plastic bag in the prepaid, pre-addressed package and seal it. Write your postal code in the six boxes in the bottom right hand corner of the return label. Do not write your name or address on the return label. Return your test in the package provided

 Animal production
Animal production Crop production
Crop production Farm business
Farm business Farm population
Farm population Food
Food Land use
Land use